Probability & Statistics
Chapter 2. Probability
Section 2.1 Sample Space
Definition 2.1
Sample Space : the set of all possible outcome of a statistical experiment
Figure 2.1 Tree diagram for Example 2.2
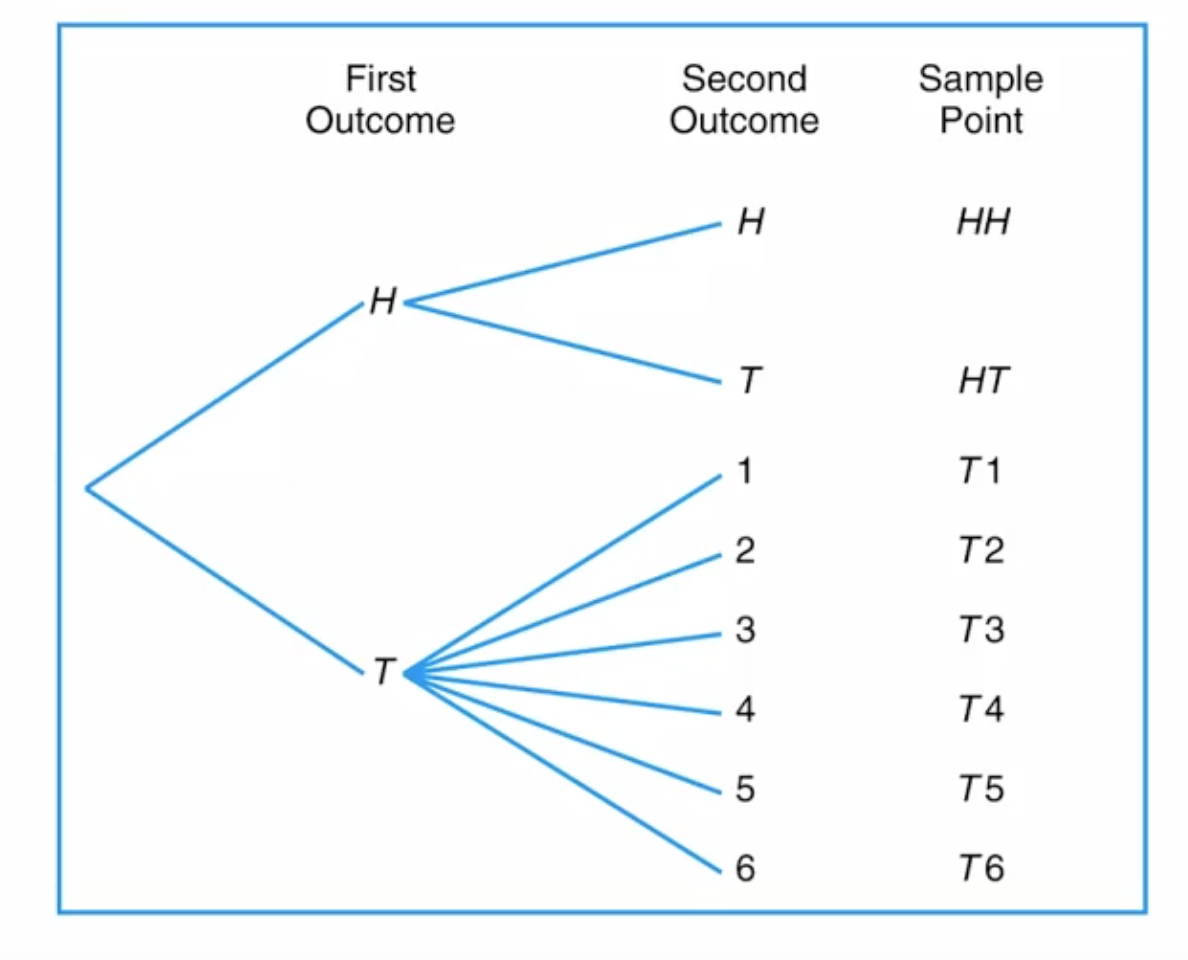
Section 2.2 Events
Definition 2.2
Event : a subset of a sample space
Definition 2.3
Comlement : an event A with respect to S is the subset of all elements of S that are not in A
Definition 2.4
Intersection : the event contating all elements that are common to A and B
Definition 2.5
Two events a and b are mutually exclusive, or disjoint, if (A∩B) = ∅, that is, if A and B have no elements in common.
Definition 2.6
The union of the two evnets A and B, denoted by the sybol A ∩ B, is the event containing all the elements that belong to A or B or both.
Figure 2.3 Events represented by various regions
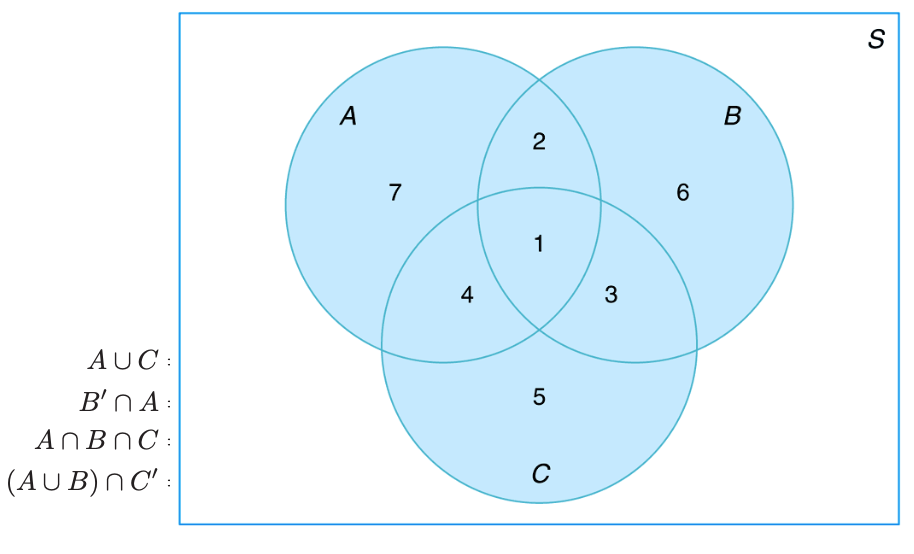
Figure 2.4 Events of the sample space S
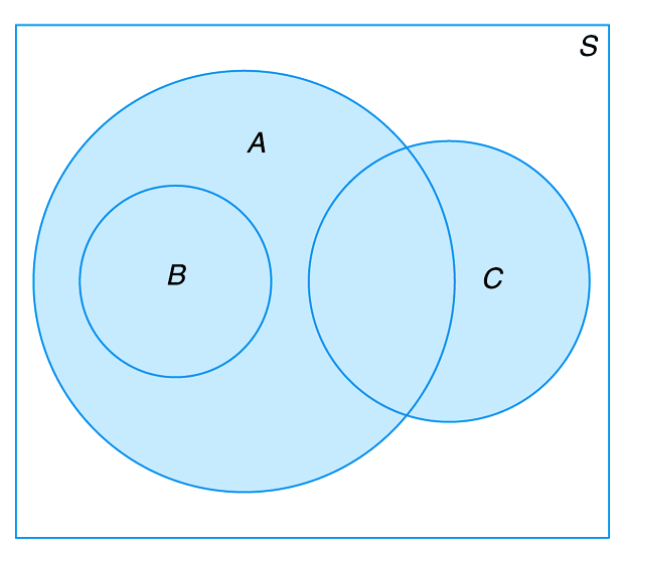
Figure 2.5 Venn diagram for Exercises 2.19 and 2.20

Section 2.3 Counting Sample Points
Rule 2.1
Multiplication rule: if an operation can be performed in n1 ways, and for each of these a second operation can be performed in n2 ways, then the two operations can be performed together in n1n2 ways
n1 + n1 + · · · + n1(n2 times ) = n1n2.
Rule 2.2

Example 2.16 ★
Q. Sam is going to assemble a computer by himself. He has the choice of chips from two brands, a hard drive from four, memory from three, and an accessory bundle from five local stores. How many different ways can Sam order the parts?
A. 2*4*3*5=120
Definition 2.7
A permutation is an arrangement of all or part of a set of object
Definition 2.8

Theorem 2.1
The number of permutation of n objects is n!
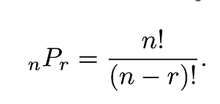
Theorem 2.2 ★
The number of permutation of n distinct objects taken r at a time is

Q. In a contest, there are 10 participants. There are three –gold, silver,
and bronze prizes for the participants. What is the total number of cases of prize reception?
A. 10P3 = 10!/(10-3)! = 10*9*8 = 720
Theorem 2.3
The number of permutation of n objects arranged in a circle is (n-1)!.
Theorem 2.4
The number of distinct permutations of n things of which n1 are of one kind, n2 of a second kind, ..., nk of a kth kind is
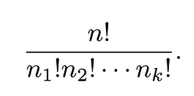
Theorem 2.5

Theorem 2.6

https://quizlet.com/_8bgx3r?x=1qqt&i=184b21
'Studies & Courses > Data Analytics & Stats' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Visualization] Intro to Data Visualization (0) | 2020.05.24 |
|---|---|
| [Probability & Statistics] 4. Bayes’ Rule, Concept of a Random Variable (2) | 2020.04.18 |
| [Probability] Intro to Statistics and Data Analysis (0) | 2020.04.18 |
| [Probability] Probability - Part 2 (0) | 2020.04.05 |
| [Probability] Probability - Part 1 (0) | 2020.04.01 |




댓글